Introduction
Bank cards are equipped with multiple layers of protection to ensure that your funds remain secure. One crucial layer is the CVC or CVV code, located on the back of the card. These codes are confidential and should only be known to the cardholder.
Bank card security levels
Bank cards incorporate several protective features to prevent unauthorized access:
- Magnetic stripe: Encodes the cardholder’s information, validity period, and other essential data.
- Barcode: Stores encrypted information differently than the magnetic stripe.
- Chip: Offers higher memory capacity and advanced encryption to enhance security.
- Owner’s signature: A handwritten element for verification purposes.
- Security code (CVC/CVV): A three-digit code printed on the back of the card to verify online transactions.
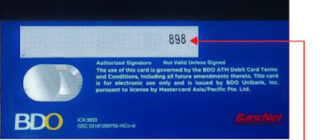
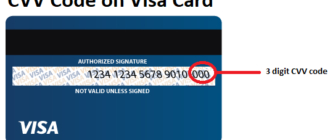
Where is the security code on a debit card?
The security code (CVC or CVV) is generally located on the back of the card, next to or on the same line as the signature panel. This code is one of the most important elements for verifying online payments and preventing fraud.
Common problems with security codes and their solutions
-
Card loss
- Problem: Losing a card exposes your security code to potential misuse by criminals.
- Solution: Immediately contact your bank to block the card and prevent unauthorized transactions.
Incorrect storage
- Problem: Storing cards in wallets or purses where the security code is visible increases the risk of theft.
- Solution: Use a secure compartment or protective case to conceal your card.
-
Online misuse
- Problem: Entering the security code on unverified or suspicious websites may lead to data theft.
- Solution: Only input your security code on trusted, secure websites. Look for SSL encryption (https://) and verified security seals.
-
Usage in restaurants and cafes
- Problem: Handing your card to a waiter who takes it out of sight can risk exposing your security code.
- Solution: Always accompany the waiter to the checkout area to oversee the transaction.
-
ATM fraud
- Problem: Using unfamiliar or counterfeit ATMs can lead to your security code being compromised.
- Solution: Use ATMs in trusted locations and avoid entering your security code on suspicious devices.
Conclusion
By understanding the role of the security code and adhering to safe practices, you can significantly reduce the risk of fraud and unauthorized access to your funds. Safeguard your card, use the security code responsibly, and remain vigilant to protect your financial assets.