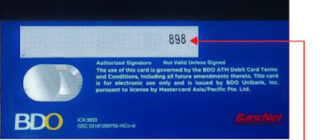
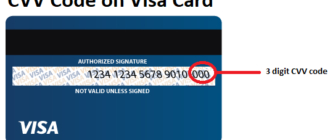
The Card Verification Code (CVC), also referred to as the Card Verification Value (CVV), is a crucial security feature implemented on credit and debit cards to enhance the safety of digital and card-not-present transactions. This code, typically a three- or four-digit number printed on the back or front of a card, is designed to confirm the cardholder’s possession of the physical card. It adds an extra layer of protection, particularly for online and telephone purchases.
The Introduction of CVC in Brazil
Brazil’s adoption of the CVC code is part of a global strategy to mitigate fraud, especially in the growing field of e-commerce. Although precise dates for its implementation in Brazil are not widely documented, it is likely that Brazilian financial institutions adopted the CVC feature in the late 1990s to early 2000s, mirroring the practices of major international payment systems such as Visa, Mastercard, and American Express.
The introduction of CVC codes coincided with Brazil’s shift toward digitization in banking and commerce, reflecting the country’s commitment to aligning with global security standards. This measure was vital in building consumer trust in a burgeoning digital marketplace.
Impact of CVC Codes on the Brazilian Economy
The implementation of CVC codes has had a transformative effect on Brazil’s economy, particularly in the areas of digital finance and e-commerce:
- Boosting Consumer Confidence:
- By significantly reducing fraud in online transactions, CVC codes have enhanced the safety of digital payments.
- This increased confidence has encouraged more Brazilians to shop online, contributing to a surge in e-commerce activity.
- Facilitating E-commerce Growth:
- Brazil is one of the largest e-commerce markets in Latin America, and the introduction of secure payment methods like the CVC code has been pivotal in this growth.
- Safer transactions have led to higher customer retention rates and expanded the reach of businesses into remote areas.
- Promoting Financial Inclusion:
- By making digital transactions more secure, CVC codes have allowed individuals who were previously hesitant about online shopping to participate in the digital economy.
- This inclusion has helped bridge gaps between urban and rural populations, fostering economic activity nationwide.
Implementation Costs for Brazilian Banks
The introduction of CVC codes in Brazil required significant investments by financial institutions. Although exact figures are not publicly available, the costs can be attributed to several key areas:
- Technological Upgrades:
- Banks needed to enhance their payment processing systems to handle CVC verification efficiently.
- This included integrating CVC verification into existing infrastructure, ensuring seamless compatibility with international payment networks.
- Employee Training:
- Financial institutions invested in educating their workforce about the functionality and importance of the CVC code.
- Training programs were essential to ensure employees could assist customers and maintain compliance with new security protocols.
- Consumer Education:
- Banks launched public awareness campaigns to educate customers about the purpose and usage of CVC codes.
- These campaigns highlighted the importance of not sharing the CVC code and only using it on secure platforms.
- Regulatory Compliance:
- Implementing the CVC code required banks to comply with international security standards, such as PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standards).
- Ensuring compliance involved additional auditing and system optimization costs.
Challenges in Implementation
While the benefits of CVC codes are clear, their implementation was not without challenges:
- Fraud Adaptation:
Fraudsters continuously evolve their methods, leading to the need for further innovations, such as dynamic CVC codes or biometric authentication. - Consumer Resistance:
- Early on, many cardholders were unfamiliar with CVC codes, leading to confusion during online transactions.
- Overcoming this barrier required extensive outreach and education efforts.
Conclusion
The integration of CVC codes into Brazil’s financial ecosystem represents a critical milestone in the country’s journey toward a secure and inclusive digital economy. By reducing fraud and enhancing trust in digital payments, CVC codes have empowered consumers and businesses alike to embrace the convenience of online transactions.
Although the costs associated with implementation—such as technological upgrades, employee training, and consumer education—were significant, the long-term benefits far outweigh these expenses. From fostering e-commerce growth to promoting financial inclusion, the CVC code has proven to be a valuable tool in modernizing Brazil’s financial system.
As Brazil continues to innovate in digital finance, the lessons learned from implementing CVC codes will serve as a foundation for future advancements in transaction security, ensuring that consumers and businesses remain protected in an ever-evolving digital landscape.