Introduction
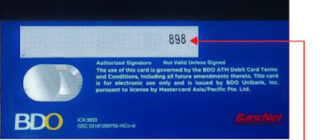
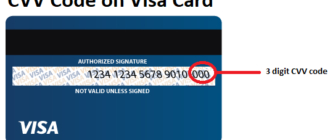
CVV2 (Card Verification Value 2) is a critical security feature designed to confirm the authenticity of a bank card during online transactions. This three- or four-digit code is located on the back of the card, near the signature panel, and is applied using embossing or ID printing. Understanding CVV2 is essential for ensuring secure financial transactions and protecting personal data from fraudsters.
What is CVV2 For?
The primary purpose of CVV2 is to verify that the individual making a purchase has physical possession of the card. This helps prevent unauthorized transactions and enhances the security of online shopping. However, not all merchants require the CVV2 code. Its usage depends on the type of card and the bank’s policies. For instance, entry-level debit cards such as Visa Electron, Mastercard Cirrus Maestro, and MasterCard Electronic may not include a CVV2 code.
Where is CVV2 Located?
CVV2 can be found on the back of the card, positioned after the cardholder’s signature. It is a discreetly printed or embossed code intended for one-time authentication during transactions. Importantly, merchants are prohibited from storing CVV2 codes even temporarily, as they are solely for instant verification.
How to Protect CVV2?
Protecting your CVV2 code is crucial to avoid falling victim to fraud. Follow these best practices to safeguard your financial information:
- Do Not Share Your CVV2: Never disclose the CVV2 code to strangers or over the phone, even if the caller claims to represent a trusted organization.
- Avoid Posting Card Photos Online: Ensure that no images of your card, including the CVV2, are shared on social media or other public platforms.
- Mask CVV2 in Card Copies: If you need to send a photocopy or scan of your card (e.g., for verification purposes with certain services), cover the CVV2 code with opaque material before sharing the image.
Alternative Authentication Methods
While CVV2 remains a widely used security feature, alternative authentication methods are gaining popularity:
- SMS Notifications: Banks often send one-time passwords (OTPs) to the customer’s registered mobile number for transaction verification. This adds an extra layer of security.
- Biometric Authentication: Some platforms allow authentication using fingerprints or facial recognition, reducing reliance on CVV2 codes.
- Secure Tokens: Digital tokens generated by banking apps or devices can serve as an alternative to CVV2 for online purchases.
Conclusion
CVV2 is a vital component of online transaction security, ensuring that only the rightful cardholder can authorize payments. By understanding its purpose and following best practices for its protection, you can minimize the risk of fraud and safeguard your financial data. As alternative authentication methods continue to evolve, CVV2 remains a reliable and essential tool for secure financial transactions.