Introduction
Visa security codes are an essential component of modern transaction security, designed to protect against fraud and ensure the authenticity of financial transactions. These codes, often referred to as CVC (Card Verification Code) or CVV (Card Verification Value), serve as a critical layer of protection in online, phone, and mail-order transactions. In this article, we explore the origin, types, and uses of Visa security codes, as well as their advantages and limitations.
The Evolution of Security Codes
The concept of security codes was born out of necessity due to the rising prevalence of credit card fraud. Initially developed in the UK in 1995, the idea involved the introduction of a unique alphanumeric code to verify cardholder authenticity. Over time, the system evolved into the simpler three-digit numeric code we use today.
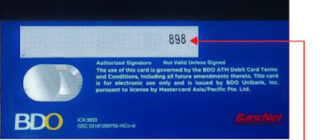
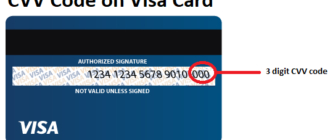
In 1997, Visa adopted the CVC2 (Card Verification Code 2) standard, placing a three-digit code on the back of cards, adjacent to the signature strip. This code is generated by encrypting the card number and expiration date using proprietary algorithms. The aim was to add an extra layer of verification, particularly for transactions where the card is not physically present.
Types of Visa Security Codes
Visa employs several types of security codes, each tailored for specific purposes:
- CVC2 (Card Verification Code 2): The three-digit code on the back of Visa cards, primarily used for online and remote transactions.
- CVV2 (Card Verification Value 2): Functionally identical to CVC2 but distinguished by regional terminology differences.
- Dynamic CVC: A newer, temporary code that changes periodically, offering enhanced security for online transactions by rendering stolen codes useless after a short period.
Applications of Visa Security Codes
Visa security codes are used in various scenarios to validate the legitimacy of transactions and ensure customer confidence. Key use cases include:
- Online Transactions: The CVC or CVV code is required during checkout to verify the cardholder’s identity and confirm the purchase.
- Phone and Mail Orders: Merchants request the security code to validate that the customer has physical access to the card.
- In-store Transactions (Limited Cases): While rare, some merchants may require the code for additional verification during suspicious or high-value purchases.
Advantages of Visa Security Codes
- Enhanced Security: Security codes provide a robust defense against unauthorized transactions by ensuring that even if the card number is stolen, the cardholder must possess the physical card to complete a transaction.
- Ease of Use: The code is conveniently located on the card and does not require additional hardware or steps for verification.
- Increased Trust: The use of security codes fosters confidence among customers and merchants, making transactions more secure.
Limitations and Risks
While security codes are a valuable tool, they are not without limitations:
- Susceptibility to Phishing: Fraudsters may use phishing emails or fake websites to trick cardholders into providing their security codes.
- System Errors: Technical glitches or system outages may prevent the proper verification of codes, leading to transaction delays.
- Static Codes: Traditional codes remain constant until the card is replaced, making them vulnerable if compromised. Dynamic codes are a more secure but less widespread solution.
Best Practices for Cardholders
To maximize the security benefits of Visa security codes, cardholders should follow these best practices:
- Keep Codes Confidential: Never share your CVC or CVV code with anyone, even if they claim to be from your bank or a trusted organization.
- Verify Websites: Ensure that you are entering your code on secure websites with HTTPS encryption.
- Monitor Transactions: Regularly review your bank statements for suspicious activities and report discrepancies immediately.
- Use Virtual Cards: For online purchases, consider using virtual cards with dynamic security codes for added protection.
- Be Alert to Scams: Avoid responding to unsolicited emails, calls, or messages asking for your card details or security code.
Conclusion
Visa security codes, such as CVC and CVV, are indispensable tools for maintaining transaction security in an increasingly digital financial landscape. They offer a simple yet effective means of preventing unauthorized access and fostering trust in the payment ecosystem. However, their effectiveness relies on users being vigilant and adopting additional security measures. As technology evolves, dynamic security codes and other innovations are poised to further strengthen the safety of financial transactions.
By understanding the role and importance of these codes, cardholders can better protect their financial data and enjoy greater peace of mind in their daily transactions.
References
- History and Evolution of Card Security Codes. (2023).
- Visa’s Implementation of CVC and CVV Standards. (2023).
- The Role of Dynamic Security Codes in Online Transactions. (2023).
- Best Practices for Transaction Security. (2023).
This comprehensive guide provides insight into the significance of Visa security codes and serves as a resource for enhancing your understanding of financial safety.