Introduction
As the use of electronic cards continues to rise, understanding the CVC (Card Verification Code) and its significance in mobile applications is crucial. The CVC is a vital security feature that ensures safe financial transactions, particularly in a digital environment. This article explores the role of the CVC in mobile applications, real-life examples of its usage, and the necessary precautions to safeguard your financial information.
What is a CVC Code?
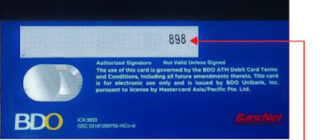
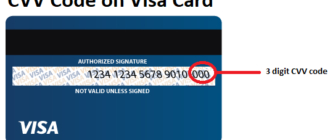
The CVC (Card Verification Code) is a three-digit code printed on the back of physical cards or digitally integrated into electronic card systems. It serves as an additional layer of security, ensuring that the individual initiating a transaction has legitimate access to the card. The CVC is primarily used for:
- Online purchases
- Money transfers
- Authentication during card-not-present transactions
This code is a critical element of the card’s security system and should remain confidential, known only to the cardholder.
Examples of CVC Code Usage in Mobile Applications
- Case 1: Anna from Moscow
Anna, an active user of a mobile banking app, frequently manages her electronic card through the platform. During an online purchase, the app requested her CVC code to confirm the transaction. After securely entering the code, her purchase was processed seamlessly. - Case 2: Dmitry from St. Petersburg
Dmitry faced a security challenge when he lost his electronic card. Thanks to his bank’s mobile application, he quickly blocked the card and ordered a replacement. The new card included a unique CVC code, which he memorized and refrained from sharing, ensuring the continued security of his financial activities.
Precautions for Using CVC Codes in Mobile Applications
To maximize the security of your CVC code while using mobile apps, consider the following best practices:
- Protect Your Device:
Avoid giving your smartphone or tablet with banking apps installed to others. A compromised device can lead to unauthorized access. - Never Share Your CVC Code:
Do not disclose your CVC code over the phone, via messaging apps, or to untrusted sources. Legitimate institutions will never request this information. - Update Your Apps Regularly:
Ensure that your mobile applications are up to date. Software updates often include security enhancements that protect against vulnerabilities. - Beware of Suspicious Websites:
Only enter your CVC code on verified and secure platforms with “https” in their URL. Avoid unknown or untrustworthy sites. - Reissue Virtual Cards Periodically:
Regularly request new virtual cards through your banking app to minimize the risk of fraud.
Why CVC Code Security Matters
The CVC code is integral to protecting electronic cards in a mobile-first world. It not only validates transactions but also reduces the risk of fraud by acting as a verification layer that criminals often cannot bypass.
However, as digital transactions grow, so do the risks. Fraudsters continually devise schemes to exploit vulnerabilities, making it vital for users to stay informed and vigilant.
Conclusion
The CVC code in mobile applications is a cornerstone of financial security for electronic cards. By understanding its role and implementing necessary precautions, users can protect themselves from fraud and unauthorized transactions.
Real-life examples like those of Anna and Dmitry illustrate the importance of knowing how to use and safeguard the CVC. By combining awareness with proactive measures, individuals can confidently use their electronic cards while ensuring the safety of their financial transactions.
Takeaway: Staying informed about the role of the CVC code and adopting robust security practices is not just recommended—it’s essential for protecting your digital financial footprint.