Introduction
- Relevance of the Topic:
In today’s digital age, security codes on debit cards are essential for safeguarding financial transactions. Understanding the legal framework surrounding their use is crucial for protecting cardholders from fraud and ensuring compliance with laws. - Purpose of the Article:
This article aims to outline the main legal norms and rules related to the use of security codes on debit cards, while offering practical advice for protecting personal data.
1. Definition and Importance of Security Codes
- What Are Security Codes?
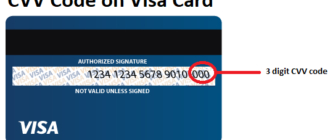
Security codes, also known as CVV (Card Verification Value) or CVC (Card Verification Code), are unique numerical combinations printed on the back of debit or credit cards. These codes act as an additional security layer, confirming the authenticity of transactions. - How Are They Used?
Security codes are primarily used in online and phone transactions to verify that the person making the purchase has physical access to the card. They play a critical role in preventing unauthorized transactions.
2. Legal Framework
- Key Laws and Regulations:
In many countries, the use of security codes is governed by national payment system laws. For instance, in the Russian Federation, the Federal Law “On the National Payment System” outlines the rules for using security codes and the responsibilities of cardholders and institutions. - Real-World Applications:
There have been notable cases where laws protecting security codes were enforced. For example, cybercriminals who accessed and misused security codes faced fines and imprisonment under relevant statutes.
3. Liability for Legal Violations
- Types of Liability:
The misuse of security codes can result in administrative or criminal penalties, including fines, imprisonment, or both, depending on the severity of the violation. - Court Case Examples:
In one instance, a fraudster was sentenced to prison for forging security codes and using them to make unauthorized transactions. The case highlighted the importance of strict regulations and enforcement.
4. Recommendations for Protecting Security Codes
- Practical Advice for Cardholders:
- Conceal Codes: Use a black marker to hide the CVV on your physical card after memorizing it.
- Block Lost or Stolen Cards: Immediately report lost cards to your bank and block them to prevent misuse.
- Avoid Public Computers: Refrain from entering card details on shared or public devices to reduce the risk of data theft.
- Successful Fraud Prevention Strategies:
Multi-factor authentication (e.g., using OTPs) and monitoring account statements regularly are effective measures to safeguard security codes.
5. International Differences in Legislation
- Varying Approaches:
Different countries have unique regulations regarding the use of security codes. For example:- United States: Stricter laws mandate robust encryption and secure storage of cardholder data.
- European Union: Implements strong customer authentication (SCA) requirements under PSD2 regulations.
- Global Case Studies:
A notable case in the UK involved a retailer fined for failing to secure CVV codes during transactions, emphasizing the importance of adhering to international standards.
Conclusion
Understanding the legal aspects of security codes on debit cards is essential for safeguarding financial transactions and avoiding legal issues. Security codes play a vital role in protecting cardholders, but they require vigilance and adherence to best practices for optimal safety.
Recommendations for Cardholders
- Regularly update your card details and passwords.
- Enable multi-factor authentication for added security.
- Be cautious when entering card information, especially on unfamiliar or untrusted websites.
By following these guidelines and staying informed about relevant laws, you can effectively protect your financial data and reduce the risk of fraud.
This comprehensive guide provides a detailed understanding of the legal and practical aspects of security codes, helping cardholders navigate the complexities of modern financial security.