Introduction
Bank cards have various security features designed to protect your finances from fraud, and among the most important are verification codes like CVV and CVC. While these codes may seem similar, they have distinct purposes and are associated with specific payment systems. This article will delve into the differences between CVV and CVC codes, explain their significance, and clarify the role of similar codes across other payment systems.
What Are CVV and CVC Codes?
CVV (Card Verification Value) and CVC (Card Verification Code) are three-digit security codes found on the back of most credit and debit cards. They serve as an additional layer of authentication when making online or remote transactions. These codes ensure that the person initiating the transaction has physical access to the card, thereby reducing the risk of unauthorized use.
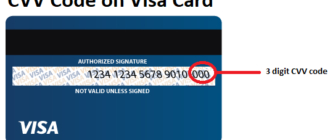
- CVV: Primarily used on Visa cards.
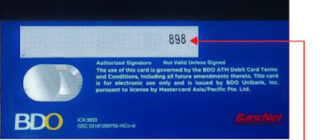
- CVC: Primarily used on Mastercard cards.
Key Differences Between CVV and CVC Codes
The main distinction between CVV and CVC codes lies in their association with specific payment systems:
- Payment System Affiliation:
- CVV: Used exclusively on Visa cards.
- CVC: Used exclusively on Mastercard cards.
- Functionality:
- Both codes serve the same purpose—verifying the authenticity of the card during transactions.
- The difference in naming reflects the internal protocols and branding of the respective payment systems.
- Technical Implementation:
- Though their purpose is identical, the encryption and generation methods may differ slightly depending on the payment system.
Why Do Cards Have Different Verification Codes?
Different payment systems have their own security codes to align with unique protocols and branding strategies. Apart from CVV (Visa) and CVC (Mastercard), other systems use their own terms for similar security features:
- Mir (Russia):
- Uses CVP (Card Verification Parameter) or PPK (Payment Processing Key) as its security code.
- UnionPay (China):
- Employs the CVN (Card Verification Number) for transactions.
- American Express:
- Features a four-digit CID (Card Identification Number) located on the front of the card.
These codes all serve the same purpose: to verify the authenticity of the card and enhance the security of transactions.
How to Access CVV/CVC for Virtual Cards
Unlike physical cards, virtual cards do not have printed codes. Instead, banks provide this information digitally:
- Access the CVV or CVC code for your virtual card through your online banking portal or mobile app.
- The code is displayed securely within your account and may be visible only temporarily for added security.
When Should You Provide CVV/CVC Codes?
Understanding when to use your CVV or CVC code is crucial to safeguarding your finances:
- When to Provide the Code:
- During online purchases to confirm transactions.
- When linking your card to secure payment platforms or apps.
- When NOT to Provide the Code:
- Never share your CVV/CVC code with third parties, even if they claim to be bank representatives.
- Avoid providing the code in surveys, questionnaires, or unsolicited requests.
- Do not include the code in written or digital documents where it can be intercepted.
Precautions to Ensure Security
- Keep It Private: Never share your CVV/CVC code with anyone, including close acquaintances.
- Verify Websites: Only enter the code on secure websites (look for “https://” in the URL) with verified reputations.
- Use Virtual Cards: For online shopping, virtual cards with unique CVV/CVC codes can provide added security.
- Monitor Transactions: Regularly review your transaction history for suspicious activity and report unauthorized transactions immediately.
Conclusion
CVV and CVC codes are essential tools for safeguarding your financial transactions. Understanding their purpose, differences, and proper usage can help you protect your funds from fraud. Additionally, being aware of other similar codes used in different payment systems enhances your financial literacy and preparedness for global transactions.
By following best practices and remaining vigilant, you can ensure that your credit and debit cards remain secure, whether you’re shopping online, paying bills, or linking your card to mobile payment platforms.
Stay informed, stay secure, and safeguard your finances with proper CVV and CVC code usage.