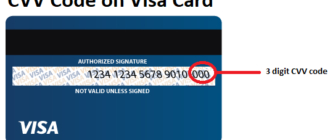
The Card Security Code (CSC), also known as CVC (Card Verification Code) or CVV (Card Verification Value), is a key feature designed to enhance the security of financial transactions. Found on the back of most credit and debit cards, the CSC plays a vital role in safeguarding cardholder information during online or card-not-present transactions. However, while the CSC offers numerous advantages, it also comes with certain limitations. This article explores the reasons to use a CSC number and the challenges associated with it.
Reasons to Use a CSC Number
- Fraud Protection
- Enhanced Security: The CSC helps protect against credit and debit card fraud, especially in transactions where the cardholder is not physically present. It adds a critical layer of verification, ensuring that the individual initiating the transaction has access to the card.
- Merchant Confidence: By requiring the CSC, merchants can reduce the likelihood of unauthorized transactions, as fraudsters often lack access to the code.
- Online Shopping Convenience
- Secure Transactions: The CSC is commonly required for online purchases and mail orders, where the cardholder cannot physically present the card. This requirement reduces the risk of fraudulent transactions involving stolen or counterfeit card details.
- Consumer Trust: Shoppers feel more secure knowing that merchants are taking steps to verify transactions through the CSC.
- Security Standards Compliance
- Adherence to PCI DSS: The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) mandates that sensitive cardholder data, including the CSC, must not be stored after a transaction is authorized. This reduces the risk of data breaches and protects both cardholders and financial institutions.
- Industry Best Practices: Compliance with these standards helps merchants build trust and credibility with customers.
- Cost Savings for Merchants
- Reduced Dispute Resolutions: Transactions that include the CSC are less likely to be disputed successfully by fraudsters. This reduces the costs associated with chargebacks and refunds for merchants.
- Lower Fraud Rates: By verifying transactions with a CSC, merchants can lower the risk of financial losses from fraudulent purchases.
Arguments Against Using a CSC Number
- Phishing Scams
- Vulnerability to Scams: The CSC does not offer protection against phishing attacks, where cardholders are tricked into entering their details, including the CSC, on fraudulent websites.
- False Sense of Security: While the CSC enhances security, it is not a comprehensive fraud prevention tool.
- Limitations for Recurring Transactions
- Inability to Store the CSC: PCI DSS regulations prohibit the storage of CSC codes after the initial transaction. This poses a challenge for merchants offering subscription-based services or recurring billing.
- Additional Customer Effort: Customers may need to re-enter their CSC for each transaction, which can be inconvenient and lead to customer dissatisfaction.
- Lack of Universality
- Not Used by All Issuers: Some card issuers do not require or support the CSC, making it inapplicable in certain cases. This creates inconsistencies for merchants handling international transactions.
- Complex Transaction Processing: Merchants may need to process transactions differently depending on whether the card issuer uses a CSC, adding complexity to their operations.
- Regional Variations
- Inconsistent Requirements: In some regions, such as North America, merchants may not always require the CSC, diminishing its effectiveness as a security tool.
- Weakened Security: Transactions that do not require a CSC are inherently less secure, increasing the risk of fraud in these areas.
Balancing Benefits and Challenges
The CSC number offers undeniable advantages in enhancing transaction security and preventing fraud. It plays a crucial role in protecting both cardholders and merchants in card-not-present transactions. However, its effectiveness is not without limitations:
- Mitigation Strategies: To address phishing scams, customers should be educated about secure browsing practices and only entering card details on trusted websites.
- Merchant Solutions: Businesses can adopt additional security measures, such as tokenization and multi-factor authentication, to complement the CSC and enhance transaction safety.
Conclusion
The CSC number remains a vital component of modern payment security, providing a valuable layer of protection for online and remote transactions. While it has certain limitations, understanding its purpose and proper usage can significantly reduce the risk of fraud. Merchants and cardholders alike must balance its benefits with its challenges to ensure a secure and seamless transaction experience. By staying informed and adopting complementary security practices, the CSC can continue to play an essential role in safeguarding financial transactions.