Introduction
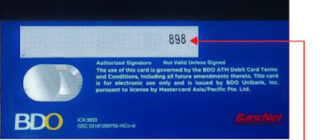
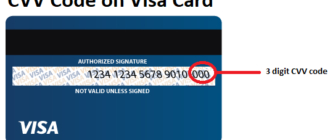
The Card Verification Value (CVV), also known as the Card Security Code (CSC), is a crucial security feature found on credit and debit cards. Designed to enhance the safety of card-not-present transactions, such as online or phone purchases, the CVV serves as an additional layer of protection. This three- or four-digit code is typically printed on the card but is not stored in the magnetic stripe or embedded chip, ensuring that only the physical cardholder can access it.
Purpose and Importance of the CVV
The CVV code plays a pivotal role in reducing fraud and ensuring the security of electronic transactions. Its primary functions include:
- Verification: The CVV confirms that the person initiating the transaction has the physical card in their possession.
- Fraud Prevention: By requiring the CVV, merchants and banks add an extra layer of defense against unauthorized transactions.
- Security in Digital Payments: The code complements other security measures, such as encryption, to protect financial data during online or phone transactions.
Public Awareness and Education
Financial institutions and credit card companies have taken significant steps to educate consumers about the CVV and its importance. Awareness efforts include:
- Bank Communications: Information about the CVV is provided during card issuance, often accompanied by detailed educational materials.
- Online Resources: Bank websites and online banking platforms feature comprehensive explanations of the CVV’s purpose and proper usage.
- Customer Service: Support representatives are trained to guide cardholders in locating and understanding the CVV, ensuring its secure use.
These initiatives aim to enhance consumer knowledge and encourage secure transaction practices.
An Unusual Anecdote Involving the CVV
In the world of online transactions, a humorous story once surfaced involving a customer who confused the CVV with their ZIP code during an online purchase. Each attempt to complete the transaction failed, leading to growing frustration. Eventually, the individual realized the mistake and shared the experience online, providing an amusing yet insightful reminder of the importance of understanding card security features.
Conclusion
The CVV code is a cornerstone of secure digital payment systems. By providing an extra layer of verification, it significantly reduces the risk of fraud. Continued education by financial institutions ensures that cardholders are informed about the purpose and proper usage of the CVV, fostering safer and more secure transaction environments. As technology evolves, the CVV remains an integral part of safeguarding electronic financial transactions.