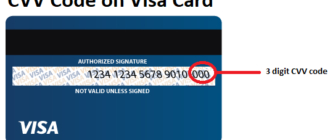
Introduction
The Card Verification Value (CVV), also referred to as the Card Verification Code (CVC), is a vital security feature introduced in the late 1990s to enhance the safety of card-not-present transactions, such as online and phone purchases. Developed by major international payment systems, including Visa and Mastercard, the CVV was created to combat the growing prevalence of credit card fraud. This article explores the adoption of the CVV in Russia, its benefits and challenges, and its role in modern electronic payment security.
The Adoption of CVV in Russia
The introduction of CVV codes in Russia coincided with the entry of international payment systems like Visa and Mastercard into the Russian financial market during the 1990s. As Russian banks began issuing cards affiliated with these systems, they incorporated CVV codes to meet international security standards. This move was pivotal in facilitating secure online transactions and modernizing the Russian banking sector.
Key milestones in CVV adoption:
- 1990s Expansion: The integration of CVV codes was aligned with the increasing availability of internet-based services and e-commerce platforms in Russia.
- Global Standardization: Russian banks embraced CVV implementation to ensure compatibility with international payment protocols and consumer protection measures.
Advantages of CVV Codes
The introduction of CVV codes brought significant advantages to cardholders, merchants, and the banking industry:
- Enhanced Security:
CVV codes add an extra layer of verification during online transactions, confirming that the cardholder physically possesses the card. This reduces the risk of unauthorized use, even if the card number is compromised. - Fraud Prevention:
By requiring the CVV for card-not-present transactions, merchants can verify the authenticity of the card. This reduces fraudulent activities such as unauthorized purchases and cloned card usage. - Boosted Consumer Confidence:
The presence of a CVV code reassures consumers about the safety of their online transactions. This trust has encouraged broader adoption of electronic payments, contributing to the growth of e-commerce in Russia. - Global Compatibility:
The integration of CVV codes ensured that Russian-issued cards could be used seamlessly in international markets, both online and offline.
Challenges and Limitations
While CVV codes have proven effective, their implementation and use have not been without challenges:
- User Awareness:
In the early stages, many cardholders were unaware of the purpose and location of the CVV code. This lack of familiarity created confusion during online transactions, necessitating widespread consumer education campaigns by banks and merchants. - Storage Restrictions:
Merchants are prohibited from storing CVV codes after transaction authorization, as per global Payment Card Industry Data Security Standards (PCI DSS). This restriction complicates processes like recurring billing, requiring users to re-enter their CVV for subsequent transactions. - Susceptibility to Fraud:
Despite its security benefits, the CVV is not foolproof. If both the card number and CVV are compromised through phishing scams or data breaches, fraudsters can exploit the information for unauthorized transactions.
The Role of CVV in Modern Payment Security
The implementation of CVV codes has significantly enhanced the security of electronic transactions in Russia. However, advancements in digital payment systems have prompted additional measures, such as tokenization, biometric authentication, and two-factor verification, to further bolster security.
Future Trends:
- Dynamic CVV Codes: Some issuers are experimenting with dynamic CVV codes that change periodically, offering enhanced protection against data theft.
- Biometric Integration: Combining CVV verification with biometric authentication can add an extra layer of security for digital transactions.
- Consumer Education: Continuous education campaigns are necessary to keep users informed about new security features and best practices for protecting their financial information.
Conclusion
The introduction of CVV codes in Russia marked a pivotal step toward improving the security of electronic payments and aligning the country’s banking practices with global standards. Despite initial challenges, such as limited user awareness and certain operational limitations, the benefits of CVV codes have far outweighed the drawbacks. They have played a critical role in preventing fraud, fostering consumer trust, and driving the growth of digital transactions.
As technology evolves, the CVV will remain an essential component of payment security, complemented by emerging innovations to address new threats. For consumers and businesses alike, understanding and utilizing this feature effectively is vital for ensuring the safety of financial transactions in an increasingly digital world.