1. Credit Card Registration
- When a customer registers for a credit card, they receive a card containing essential information, including a unique card number, expiration date, and security codes like the CVC (Card Verification Code).
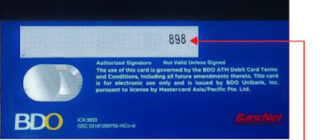
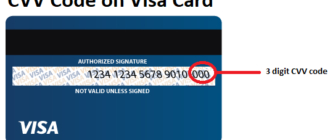
- The CVC is a three-digit code located on the back of the card, near or within the signature panel. It is not stored in the card’s magnetic stripe or chip, ensuring additional security.
2. Card Usage
- In-Store Purchases: The cardholder physically presents the card for payment at point-of-sale terminals.
- Online Transactions: When making online purchases or transfers, the system requires the card number, expiration date, and the CVC code for additional verification. This confirms that the cardholder has the physical card in their possession.
3. Transaction Verification
- During online purchases or fund transfers:
- The system prompts the user to enter the card details, including the CVC code.
- If the CVC code is entered correctly, the system validates the card’s authenticity and approves the transaction.
- If the CVC is incorrect, the transaction is blocked, safeguarding against unauthorized activities.
4. Fraud Protection
- The CVC code adds an essential layer of security by confirming that the individual initiating the transaction possesses the physical card.
- Fraudsters cannot complete transactions without the correct CVC, significantly reducing the risk of financial theft or fraud.
- This mechanism protects the cardholder’s funds and sensitive information from being compromised.
5. Notifications and Monitoring
- Most credit card issuers provide real-time notifications for transactions via mobile banking apps or email alerts. This helps cardholders stay informed about account activity.
- Cardholders can monitor their transaction history to identify any suspicious activity promptly.
- If the card is lost or compromised, the cardholder can block it immediately through the banking app or by contacting customer service.
6. Precautions for Cardholders
To maximize the security of the CVC code and the credit card, follow these best practices:
- Do Not Share the CVC: Avoid disclosing the CVC code to anyone, including over phone calls, emails, or untrusted websites.
- Use Trusted Platforms: Only enter card details on secure websites with “https://” in the URL and verified payment gateways.
- Leverage Additional Security Features: Enable 3D Secure or other multi-factor authentication methods provided by your bank.
- Regularly Update Card Information: Periodically review and update linked accounts, ensuring no unauthorized users have access.
- Be Vigilant Against Phishing: Do not respond to unsolicited requests for your card details, even if they appear legitimate.
Conclusion
The CVC code plays a critical role in securing credit card transactions by preventing unauthorized use and reducing fraud risks. From verifying transactions to enhancing fraud protection, this small but vital feature ensures the safety of cardholders’ financial data. By understanding the role of CVC and adopting security measures, cardholders can confidently use their credit cards for both in-store and online transactions.