1. Understanding CVV Codes: A Technical Overview
Card Verification Values (CVVs) are essential security features used to prevent unauthorized transactions. These codes are printed on credit and debit cards as a mechanism to authenticate transactions in scenarios where the cardholder is not physically present, such as online or over-the-phone purchases. CVVs act as an additional layer of security by confirming that the person attempting the transaction possesses the actual card, as opposed to just the card number and expiration date.
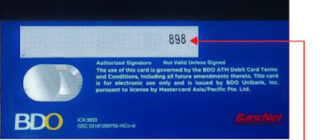
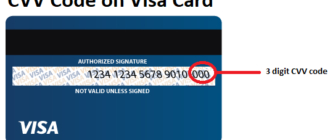
Technically, CVVs are three-digit numbers on the back of most cards (Visa, MasterCard, and Discover) or four-digit numbers on the front of American Express cards. These values are not stored in the card’s magnetic stripe or EMV chip, making them inaccessible through most physical skimming devices. Instead, CVVs are generated using complex cryptographic algorithms that take into account the card number, expiration date, and a secret key known only to the issuing bank. This ensures that the CVV is unique to each card and difficult to replicate.
The cryptographic process underpinning CVV generation involves hashing and encryption, providing a robust defense against tampering or forgery. When a CVV is submitted during a transaction, it is validated by the issuer’s systems without being stored in merchant databases, reducing the risk of data breaches.
Despite these protections, CVVs remain vulnerable to phishing attacks and social engineering. Cybercriminals often target unsuspecting individuals to extract CVV details, which can then be used for fraudulent activities. This highlights the importance of consumer awareness and the need for advanced fraud detection systems that monitor for suspicious activities.
2. The Evolution of CVV in Payment Systems
The CVV code’s introduction revolutionized online transactions by addressing vulnerabilities in card-not-present (CNP) transactions. This article explores the historical context that led to the creation of CVV codes, tracing their development alongside advancements in financial technology and fraud prevention strategies.
3. How CVVs Strengthen Security for AMEX Cards
American Express (AMEX) cards utilize a four-digit CVV, distinguishing them from the three-digit codes on Visa and MasterCard. This piece examines how AMEX’s unique approach enhances card security, its integration into broader fraud prevention measures, and why these distinctions matter.
4. The Legal Implications of Sharing CVV Numbers
This article examines the legal frameworks governing the misuse of CVV numbers. It reviews cases involving data breaches and online fraud, highlighting the penalties associated with sharing or misusing CVV codes. The piece also outlines international differences in legislation.
5. Cryptographic Protections for CVV Numbers in Digital Wallets
Digital wallets have redefined payment security. This article investigates how CVV codes are integrated into these technologies, focusing on encryption, tokenization, and the role of CVVs in securing NFC-based payments.
Journalistic Articles
6. What Does CVV Mean, and Why Is It Important?
In an era of growing online transactions, understanding the CVV code is crucial for consumers. This article explains what a CVV is, why it’s printed on credit and debit cards, and how it protects users from fraud.
7. The Dark Web’s Obsession with Free Credit Card Numbers and CVVs
The demand for stolen credit card data, including CVV codes, fuels a thriving black market. This investigative piece uncovers how criminals obtain and sell this information, the implications for victims, and measures being taken to combat this illicit trade.
8. What Does CVV Mean for the Future of Digital Payments?
With the rise of biometric and token-based authentication, is the CVV code becoming obsolete? This forward-looking article examines the potential evolution of payment security technologies and the role CVVs may play in the future.
9. Protecting Your CVV: Practical Tips for Consumers
This piece offers actionable advice for safeguarding CVV numbers. It includes tips on recognizing phishing attempts, using secure payment platforms, and why consumers should avoid sharing CVVs over unsecured channels.
10. CVV Codes and E-Commerce: Ensuring Trust in Online Transactions
E-commerce platforms rely heavily on CVV codes to verify customer identities. This article highlights how CVV codes enhance trust between merchants and consumers while examining challenges such as friendly fraud and false declines.