Introduction
In the digital age, where online transactions are an everyday necessity, the CVV code (Card Verification Value) plays a crucial role in ensuring the security of financial transactions. This three-digit code, located on the back of your credit card, acts as an additional safeguard against unauthorized use. Understanding how to use it correctly and take precautions can significantly reduce the risk of fraud.
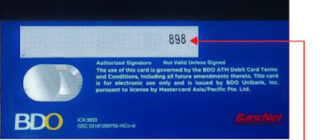
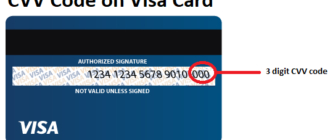
Where is the CVV Code Located?
The CVV code can be found on the back of your credit card, typically near the signature strip or next to the magnetic stripe. It is a three-digit number (or four digits for American Express cards) designed to provide additional verification for card-not-present transactions.
How to Use the CVV Code
The CVV code is primarily used during online or remote transactions to verify that the person initiating the payment possesses the physical card. Below are some common scenarios where the CVV code is required:
- Online Purchases:
- While shopping online, you’ll be prompted to enter the CVV code along with the card number and expiration date to confirm your identity and authorize the payment.
- E-Wallet Top-Ups:
- When adding funds to an e-wallet, the platform may request your CVV code to ensure the transaction is secure.
- Over-the-Phone Transactions:
- For phone-based payments, merchants may ask for the CVV code as part of the verification process.
- Recurring Payments:
- Some subscriptions or recurring payment platforms may request the CVV code during initial setup for added security.
Best Practices and Precautions
While the CVV code enhances the security of transactions, improper handling can expose your financial data to risks. Follow these precautions to safeguard your information:
- Never Share Your CVV Code:
- Do not disclose your CVV code to anyone, even if they claim to be from your bank or a trusted organization.
- Verify Website Security:
- Before entering your CVV code, ensure the website is secure. Look for the padlock symbol in the browser’s address bar and confirm the URL starts with “https://.”
- Avoid Public Wi-Fi:
- Refrain from entering your card details, including the CVV code, while connected to public or unsecured Wi-Fi networks.
- Monitor Transactions Regularly:
- Frequently check your bank and credit card statements for unauthorized transactions. Early detection can help prevent significant losses.
- Use Virtual Cards for Online Transactions:
- Some banks offer virtual cards with dynamic CVV codes, which provide an additional layer of security for online purchases.
- Store Your Card Securely:
- Keep your card in a safe and secure location to prevent physical theft or unauthorized access.
- Be Cautious with Emails and Phone Calls:
- Fraudsters often pose as legitimate entities to trick you into revealing your CVV code. Be vigilant and avoid sharing your information through unsolicited communications.
Why is the CVV Code Important?
The CVV code serves as a critical security layer, ensuring that even if someone obtains your card number, they cannot use it without the CVV code. Its purpose is to:
- Prevent Fraud: By requiring the CVV code for transactions, merchants can verify the cardholder’s authenticity.
- Ensure Secure Transactions: The code acts as a PIN for online purchases, providing an added layer of trust.
- Boost Consumer Confidence: Knowing their transactions are protected encourages users to engage in online commerce without fear.
Conclusion
The CVV code is a cornerstone of credit card security, designed to protect your financial transactions and personal information. By understanding its role, using it appropriately, and following the recommended precautions, you can minimize the risk of fraud and unauthorized use. Stay informed and vigilant to ensure a safe and secure payment experience.
Remember: Your CVV code is your card’s last line of defense. Protect it like you would any other valuable information.