Introduction
The CVV (Card Verification Value) is a three-digit security code designed to protect the identity of a debit or credit card owner during online transactions. Acting as an additional layer of security, the CVV helps prevent fraud and ensures the safety of your financial transactions.
What is CVV?
CVV stands for Card Verification Value, a code unique to each card. Depending on the payment system, it may have other names:
- CVC (Card Verification Code) for Mastercard cards.
- CVP (Card Verification Parameter) for Mir cards.
- CVN (Card Verification Number) for UnionPay cards.
Despite the differences in names, these codes serve the same purpose—enhancing the security of your financial transactions.
Where Can You Find the CVV?
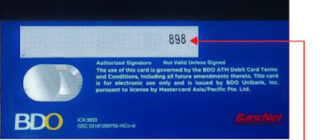
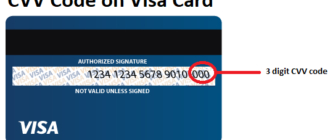
The CVV is typically located on the back of your card, near the magnetic strip. It is printed in a special field next to the cardholder’s signature. On some cards, the CVV may be located on the front, but this is less common.
Why is the CVV Important?
The CVV code plays a vital role in safeguarding your financial data, especially during online transactions. Here’s why it’s crucial:
- Fraud Prevention: The CVV ensures that only the rightful cardholder can complete transactions, adding an extra layer of protection.
- Identity Verification: When shopping online, the CVV confirms the card’s authenticity, preventing unauthorized use.
How to Use the CVV Code
When making online purchases, you will be required to enter your CVV code during the payment process. This step ensures that the card is in the hands of its rightful owner. If you are using a virtual bank card, the CVV code will also be provided and required for verification.
Examples of CVV Usage
Here are common scenarios where you’ll need your CVV:
- Online Shopping
- During checkout, you’ll be asked to input the CVV code along with your card details to confirm the purchase.
- Using a Virtual Card
- When paying with a virtual card, you will need the CVV to complete the transaction securely.
- Two-Factor Authentication
- In transactions that involve 3D-Secure technology, you may need to enter a one-time password (OTP) sent via SMS along with your CVV for additional verification.
How to Protect Your CVV Code
To safeguard your CVV and prevent unauthorized access to your financial data, follow these essential tips:
- Never Share Your CVV
- Your CVV is confidential and should not be shared with anyone, including bank employees.
- Keep Your Card Secure
- Always keep your card with you and never leave it unattended in public places.
- Obscure Your CVV
- If you’re concerned about physical theft, consider blacking out the CVV code with a marker after memorizing it. This reduces the risk of someone copying your card details.
Conclusion
The CVV code is a simple yet powerful tool for ensuring the security of your financial transactions. By understanding its purpose and following basic safety practices, you can minimize the risk of fraud and keep your funds protected. Treat your CVV with the same care as your PIN code, and enjoy a safer online shopping experience.