1. Registration and Account Verification
- User Registration: The user creates an account on the platform by providing essential information such as name, email address, phone number, and, in some cases, a valid credit card.
- Account Verification: The platform validates the provided information using secure methods, including email or SMS verification, to confirm the user’s identity and activate the account.
2. Generation of the CC Security Code
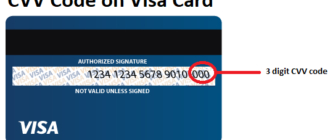
- Unique Code Creation: Upon successful registration and verification, the system generates a unique CC security code. This code, usually three or four digits, acts as an additional authentication layer.
- Delivery of the Code: The generated security code is securely sent to the user via email, SMS, or displayed on the platform’s interface for immediate use.
3. Utilization of the CC Security Code
- Authentication and Authorization: The user inputs the CC security code during sensitive actions such as:
- Logging into the account from a new device or location.
- Authorizing online transactions or fund transfers.
- Changing critical account settings like passwords or linked financial accounts.
- Identity Confirmation: The platform verifies the entered code to ensure the actions are performed by the legitimate account holder.
4. Data Encryption and Protection
- Enhanced Security: The CC security code is used to encrypt the user’s personal and financial data, ensuring secure storage and transmission.
- Secure Access: Encrypted data can only be decrypted when the correct security code is used, protecting against unauthorized access.
5. Real-Time Monitoring and Auditing
- Activity Monitoring: The system continuously tracks activities related to the use of CC security codes to detect anomalies or suspicious behavior.
- Alerts and Account Suspension: If unusual activity is identified, the platform immediately sends an alert to the user and may temporarily suspend the account to prevent potential fraud.
6. Code Updates and Revocation
- Code Expiry: Security codes are valid for a limited period to minimize risks. Expired codes are automatically invalidated.
- User Notification: Users receive timely alerts about upcoming expirations or changes to their security codes to ensure uninterrupted access.
- Manual Revocation: Users can manually revoke or request a new security code in case of suspected compromise.
7. Access Recovery
- Forgotten Code Assistance: Users who lose or forget their security codes can initiate a recovery process. This typically involves:
- Providing secondary verification, such as answering security questions or uploading identification documents.
- Receiving a temporary code or a reset link to restore access securely.
- Guided Process: The platform ensures a streamlined recovery process with clear instructions, minimizing inconvenience for the user.
Benefits of These Steps
- Enhanced Security: The CC security code provides an additional safeguard against unauthorized access and fraud.
- User Confidence: By ensuring data protection, the platform builds trust with users, encouraging them to engage in online transactions confidently.
- Regulatory Compliance: Employing such secure practices aligns with global data protection standards and regulations.
Conclusion
The implementation of a CC security code as part of the service not only secures transactions but also demonstrates a commitment to protecting user data. By following these detailed steps, platforms can offer robust security features, ensuring user trust and satisfaction while minimizing risks of financial fraud.