Introduction
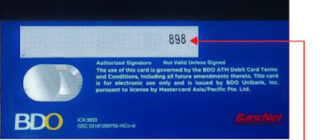
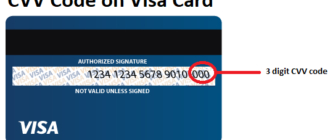
The CVV (Card Verification Value), also referred to as CVC (Card Verification Code), is an essential component of credit card security. This three-digit code, located on the back of the card near the signature strip, serves as an additional layer of protection to verify the cardholder’s identity during transactions. Its role in preventing unauthorized use of your card cannot be overstated. In this article, we’ll explore the importance of the CVV, how it works, and practical steps to safeguard it.
What is the CVV and Where Can You Find It?
The CVV is a unique security code that complements your card’s primary details (such as the card number and expiration date).
- For Visa, Mastercard, and Discover cards: The CVV is typically a three-digit code printed on the back of the card, near the magnetic strip or signature strip.
- For American Express cards: The CVV is a four-digit code printed on the front of the card, above the card number.
Although small in size, this code is a powerful deterrent against fraud.
How Does the CVV Enhance Security?
The CVV is primarily used for transactions where the card cannot be physically swiped or inserted, known as card-not-present transactions. Examples include:
- Online Purchases: When shopping on an e-commerce platform, you are often required to enter the CVV along with other card details to verify your identity.
- Phone Orders: For purchases made over the phone, merchants may ask for the CVV to ensure the person placing the order has physical possession of the card.
- Subscription Services: Many recurring payment systems request the CVV during the initial setup to authenticate the cardholder.
Why Protecting Your CVV is Crucial
The CVV acts as a safeguard against unauthorized transactions. If fraudsters gain access to your card number and expiration date but lack the CVV, they are typically unable to complete transactions. However, sharing your CVV—even unintentionally—can put you at significant risk of financial fraud.
Security Best Practices for Your CVV
- Never Share Your CVV:
- Avoid giving your CVV over the phone or email, even if someone claims to be from your bank or a merchant.
- Be cautious of phishing scams where fraudsters pose as trusted entities to steal your CVV.
- Secure Your Card:
- Keep your card in a safe location to prevent physical theft.
- Avoid storing photos of your card or its details on your phone or in easily accessible locations.
- Use Virtual Cards:
- Consider using virtual cards for online transactions. These cards generate a temporary CVV, providing an additional layer of protection.
- Verify Website Security:
- Ensure that the website you’re using is secure (look for “https” in the URL) before entering your card details.
- Monitor Transactions:
- Regularly check your bank statements for unauthorized or suspicious transactions.
- Set up transaction alerts to receive real-time updates on card usage.
Common Myths About CVV
- “Merchants Can Store My CVV for Future Use.”
- False. Payment Card Industry Data Security Standards (PCI DSS) prohibit merchants from storing CVV codes after a transaction is processed. This reduces the risk of breaches.
- “CVV Alone Can Authorize Transactions.”
- Incorrect. The CVV works in conjunction with other card details, such as the card number and expiration date, to complete a transaction.
- “Sharing My CVV with Customer Support is Safe.”
- Never share your CVV, even with customer support representatives. Legitimate entities will not ask for this code.
Conclusion
The CVV on your credit card is a critical element of your financial security, designed to reduce the risk of fraud and unauthorized transactions. By understanding its purpose and adhering to safety precautions, you can protect your finances and maintain peace of mind in the digital age.
Remember, safeguarding your CVV is a shared responsibility between you and your financial institution. Stay vigilant, take proactive measures, and ensure that your financial data remains secure.
Stay safe, stay informed, and protect your financial future!