Introduction
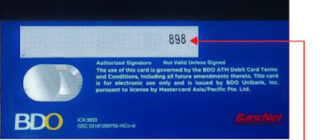
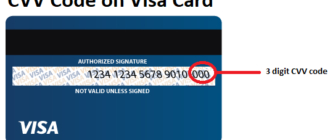
The CVV (Card Verification Value) or CVC (Card Verification Code) is a three-digit security code printed on the back of credit cards, next to the magnetic strip. This small yet powerful tool plays a critical role in verifying the identity of the cardholder and ensuring secure financial transactions, particularly for online and remote purchases. In this article, we delve into the significance, functionality, and best practices for using and protecting your CVV code.
History and Development
The concept of the CVV was introduced in the 1990s as a response to the increasing prevalence of card-not-present (CNP) fraud. Initially implemented on debit cards, it quickly became a standard security feature for credit cards. This simple yet effective solution significantly reduced unauthorized transactions and bolstered consumer confidence in online payment systems. Its widespread adoption has since contributed to the rapid growth of e-commerce globally.
How the CVV Works
The CVV is a unique, randomly generated three-digit code assigned to each credit card by the issuing bank. Unlike the card number and expiration date, the CVV is not stored in the card’s magnetic stripe or chip, making it an exclusive physical feature. Here’s how it works during a transaction:
- Authentication: When making an online or remote payment, the system prompts you to enter the CVV along with other card details.
- Verification: The entered CVV is cross-verified with the issuing bank’s records.
- Approval or Denial: If the CVV matches the bank’s records, the transaction is approved. If not, it is declined, protecting the user from potential fraud.
Benefits of Using a CVV Code
- Enhanced Fraud Protection:
- The CVV acts as a safeguard against unauthorized use by ensuring the physical possession of the card during transactions.
- It provides a second layer of defense beyond the card number and expiration date.
- Consumer Confidence:
- The CVV fosters trust in online shopping platforms, enabling users to make purchases with reduced fear of data theft.
- Its implementation has been pivotal in the rise of digital commerce.
- Ease of Use:
- Entering the CVV is straightforward and does not involve complex technical processes, making it a user-friendly security feature.
Potential Risks and Precautions
Despite its effectiveness, the CVV is not entirely immune to fraud, especially in cases of data breaches or phishing attacks. To mitigate risks, users should follow these best practices:
- Never Share Your CVV:
- Only the cardholder should know the CVV. Never disclose it over the phone, email, or messaging platforms, even if the request seems legitimate.
- Secure Your Card:
- Avoid leaving your card unattended in public places. Consider covering the CVV with a removable label for added security when not in use.
- Use Virtual Cards:
- Virtual cards generate a temporary CVV, offering a secure option for online transactions without exposing your primary card details.
Practical Examples of CVV Usage
- Online Shopping:
- While purchasing clothes, electronics, or groceries online, the CVV is required to confirm your transaction, ensuring the cardholder’s identity.
- Subscription Services:
- When signing up for subscription-based platforms, the CVV serves as an additional verification step to authorize recurring payments.
- Phone Orders:
- For phone transactions, businesses may request the CVV to confirm the authenticity of the cardholder and ensure secure payments.
Conclusion
The CVV on a credit card is more than just a three-digit number—it is a vital component of modern financial security. It helps prevent unauthorized transactions, bolsters consumer trust in digital commerce, and contributes to the overall safety of the financial ecosystem. However, its effectiveness depends on user vigilance and adherence to security practices.
Recommendations
To maximize the benefits of the CVV and protect your financial data:
- Memorize your CVV and avoid storing it in vulnerable locations.
- Utilize virtual cards for online shopping to reduce exposure to risks.
- Regularly monitor your transaction history for any suspicious activities.
- Ensure websites are secure (look for HTTPS) before entering card details.
By staying informed and proactive, you can safeguard your finances and enjoy seamless, secure transactions in the digital age.