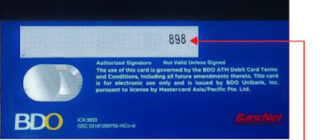
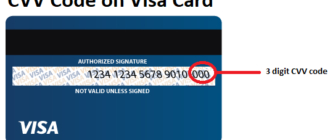
- The Card Verification Value (CVV), also known as the Card Verification Code (CVC) or Card Security Code (CSC), is a security feature found on credit and debit cards. This code enhances the security of transactions, particularly those conducted without the physical presence of the card, such as online or phone purchases.
Purpose of the CVV on Debit and Credit Cards
The primary function of the CVV is to verify that the person initiating a transaction possesses the physical card, thereby reducing the risk of unauthorized use. When making a purchase where the card is not physically swiped or inserted—known as a card-not-present transaction—merchants typically request the CVV to confirm the cardholder’s authenticity.
Differences Between Debit and Credit Cards Regarding CVV
While both debit and credit cards utilize CVVs for security, there are subtle differences in their application:
- Debit Cards: The CVV on a debit card protects funds directly from the cardholder’s bank account. Unauthorized access can lead to immediate financial loss, making CVV protection crucial.
- Credit Cards: For credit cards, the CVV safeguards the cardholder’s credit line. While fraudulent charges may not immediately impact the cardholder’s bank account, they can affect credit limits and require resolution with the issuer.
Advantages of the CVV
- Enhanced Security: The CVV adds an extra layer of protection for online and phone transactions, ensuring that the cardholder has physical possession of the card.
- Fraud Prevention: By requiring the CVV, merchants can reduce the likelihood of fraudulent transactions, as possessing the card number alone is insufficient for unauthorized purchases.
Disadvantages of the CVV
- Limited Protection: While the CVV enhances security, it is not foolproof. Fraudsters can still obtain the CVV through phishing scams or physical theft of the card.
- Inconvenience for Cardholders: Cardholders must have physical access to their cards to retrieve the CVV, which can be inconvenient if the card is not readily available.
Conclusion
The CVV is a vital component in the security framework of both debit and credit cards, providing an additional layer of protection against unauthorized transactions. While it is not an absolute safeguard, the CVV significantly enhances the security of card-not-present transactions, benefiting both consumers and merchants.